FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF TATA MOTORS FINANCE LTD (AS PER INDIAN GAAP)
During Fiscal 2017, TMFL earned a total income of R2,721.25 crores compared to Rs. 3,228.57 crores earned in Fiscal 2016, reflecting a decrease of 15.7%. The expansion of spoke branches (Tier 2 and 3 towns) has helped in reaching out to the customer more quickly and in improving customer satisfaction. The loss before tax was Rs. 698.56 crores in Fiscal 2017 as compared to a profit of Rs. 301.64 crores in Fiscal 2016. The loss after tax was Rs. 1,182.29 crores in Fiscal 2017, as compared to a profit of Rs. 267.03 crores in previous year.
FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF TATA DAEWOO COMMERCIAL VEHICLES (AS PER KOREAN GAAP)
In Fiscal 2017, TDCV's total revenue increased by 17.3% to KRW1,031.77 billion (Rs. 5,986 crores) compared to KRW879.66 billion (Rs. 5,096 crores) in Fiscal 2016, mainly due to lower export sales partially offset by increase in domestic sales. The profit after tax was KRW50.25 billion (Rs. 290 crores) compared to KRW45.56 billion (Rs. 264 crores) of previous year. Better profitability of Euro 6 Vehicles, better mix, favorable exchange realizations, continuous material cost reduction, various cost control and inventory initiatives helped in improving profits.
FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF TATA TECHNOLOGIES LTD
The consolidated revenue of TTL in Fiscal 2017 increased 4.4% to Rs. 2,801.95 crores, compared to Rs. 2,683.38 crores in Fiscal 2016. The profit before tax decreased by 2.3% to Rs. 452.77 crores in Fiscal 2017, compared to Rs. 463.53 crores in Fiscal 2016. The profit after tax decreased by 7.8% to Rs. 353.59 crores in Fiscal 2017, as compared to Rs. 383.56 crores in Fiscal 2016.
INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEMS AND THEIR ADEQUACY
The Company has an adequate system of internal controls in place. It has documented policies and procedures covering all financial and operating functions. These controls have been designed to provide a reasonable assurance with regard to maintaining of proper accounting controls for ensuring reliability of financial reporting, monitoring of operations, protecting assets from unauthorized use or losses, compliances with regulations. The Company has continued its efforts to align all its processes and controls with global best practices.
Some significant features of the internal control of systems are:
- The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors, comprising of independent directors and functional since August 1988, regularly reviews the audit plans, significant audit findings, adequacy of internal controls, compliance with accounting standards as well as reasons for changes in accounting policies and practices, if any;
- Documentation of major business processes and testing thereof including financial closing, computer controls and entity level controls, as part of compliance programme towards Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as required by the listing requirements at New York Stock Exchange;
- An ongoing programme, for the reinforcement of the Tata Code of Conduct is prevalent across the organization. The Code covers integrity of financial reporting, ethical conduct, regulatory compliance, conflicts of interest's review and reporting of concerns.
- State-of-the-art Enterprise Resource Planning, supplier relations management and customer relations management connect the Company's different locations, dealers and vendors for efficient and seamless information exchange. The Company also maintains a comprehensive information security policy and undertakes continuous upgrades to its IT systems;
- Detailed business plans for each segment, investment strategies, year-on-year reviews, annual financial and operating plans and monthly monitoring are part of the established practices for all operating and service functions;
- A well-established, independent, multi-disciplinary Internal Audit team operates in line with governance best practices. It reviews and reports to management and the Audit Committee about compliance with internal controls and the efficiency and effectiveness of operations as well as the key process risks. The scope and authority of the Internal Audit division is derived from the Internal Audit Charter, duly approved by the Audit Committee; and Anti-fraud programmes including whistle blower mechanisms are operative across the Company.
The Board takes responsibility for the overall process of risk management throughout the organization. Through an Enterprise Risk Management programme, the Company's business units and corporate functions address risks through an institutionalized approach aligned to the Company's objectives. This is facilitated by internal audit. The Business risk is managed through cross-functional involvement and communication across businesses. The results of the risk assessment are presented to the senior management. The Risk Management Committee reviews business risk areas covering operational, financial, strategic and regulatory risks.
During Fiscal 2017, the Company conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of the Internal Control over Financial Reporting and has determined that the Company's Internal Control over Financial Reporting as at March 31, 2017 is effective.
HUMAN RESOURCES / INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS
The Company considers its human capital a critical factor to its success. Under the aegis of Tata Sons and the Tata Sons promoted entities, the Company has drawn up a comprehensive human resource strategy, which addresses key aspects of human resource development such as:
- The code of conduct and fair business practices;
- A fair and objective performance management system linked to the performance of the businesses which identifies and differentiates employees by performance level;
- Creation of a common pool of talented managers across Tata Sons and the Tata Sons promoted entities with a view to increasing their mobility through job rotation among the entities;
- Evolution of performance based compensation packages to attract and retain talent within Tata Sons and the Tata Sons promoted entities; and
- Development and delivery of comprehensive training programs to impact and improve industry- and/or function-specific skills as well as managerial competence.
In line with the Company human resource strategy, it has implemented various initiatives in order to build better organizational capabilities that the Company believe will enable it to sustain competitiveness in the global marketplace. The Company's focus is to attract talent, retain the better and advance the best. Some of the initiatives to meet this objective include:
- Development of an agile organization through process modification, delayering and structure alignment and increase in customer facing roles;
- Changed organization structure has empowered teams, across each product lines, which will manage the product lifecycle and be accountable for the Profit and Loss;
- Extensive process mapping exercises to benchmark and align the human resource processes with global best practices;
- Outsource transactional activities to an in house back office (Global Delivery Center), thereby reducing cost and time of transaction;
- Talent management process redesigned with a stronger emphasis on identifying future leaders;
- Build strategic partnerships with educational institutions of repute to foster academia based research and provide avenues for employees to further their educational studies;
- Enhance company's image and desirability amongst the target engineering and management schools, to enable it to attract the best;
- Functional academies setup for functional skills development; and
- Skill development of all Blue collared workforce to enable them to effectively meet the productivity and quality deliverables.
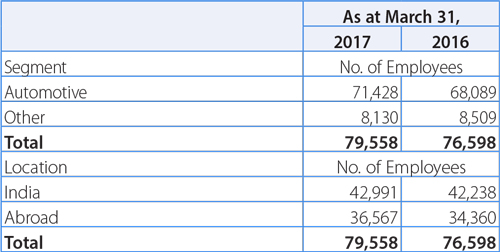
The Company employed approximately 80,389 and 76,598 permanent employees as at March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The average number of flexible (temporary, trainee and contractual) employees for Fiscal 2017, was approximately 38,692 (including joint operations) compared to 40,205 in Fiscal 2016.
The following table set forth a breakdown of persons employed by the Company's business segments and by geographic location as at March 31, 2017 and 2016.
Training and Development The Company has committed to the development of its employees to strengthen their functional and leadership capabilities. The Company have a focused approach with the objective of addressing all capability gaps and preparing its employees to adopt to fast changing external environment in order to meet its strategic objectives.
To achieve this, the Company has established the Tata Motors Academy, which addresses development needs of various segments of its workforce through a structured approach. The Tata Motors Academy focuses on three functional pillars – customer excellence, product leadership, and operational excellence – and one pillar on management education, all of which are aligned with the Company-level strategic objectives. The emphasis of functional academies is to strengthen knowledge, skills and expertise with an in depth approach, and the emphasis of management education is developing general management skills.
In addition to the Tata Motors Academy, the Company's Learning Advisory Council, which includes senior leaders from different parts of organization, aims to more closely align its learning and development efforts with its business needs and priorities. The Learning Advisory Council is responsible for designing, implementing and reviewing the learning agenda.
The Company is now migrating from a trade-based training approach to a process-based training approach, which emphasizes team members' knowledge as related to their actual work, in addition to the general trade-based skills, which are learned at training institutes. These skills are very specific and not currently taught at the training institutes. To accomplish this, the Company is implementing a fundamental skills training initiative throughout organization. Its objective is to address key employee performance issues, such as inconsistent quality, poor craftsmanship, high frequencies of repair reworking and low productivity levels through training of front-line team members.
Union Wage Settlements The Company has labour unions for operative grade employees at all its plant across India, except Dharwad plant. The labour union at Sanand plant has recently been registered and the first settlement is yet to be done. The Company has generally enjoyed cordial relations with its employees at its factories and offices and have received union support in the implementation of reforms that impact safety, quality, cost erosion and productivity improvements across all locations.
Employee wages are paid in accordance with wage agreements that have varying terms (typically three to four years) at different locations. The expiration dates of the wage agreements with respect to various locations/subsidiaries are as follows:
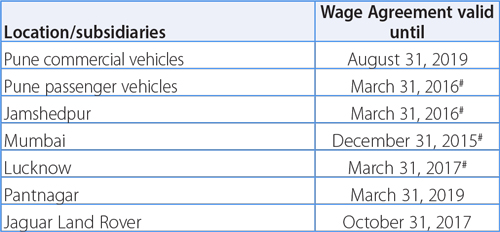
# Under negotiation
An amicable settlement has been arrived at the Pantnagar plant in May 2016 and in Pune CVBU Plant in March 2017. Negotiations are underway for new wage agreements at locations where it has expired. In the interim, the wages set forth in the previous wage agreements will continue until a new settlement is reached.
The Company's wage agreements link an employee's compensation to certain performance criteria that are based on various factors such as quality, productivity, operating profit and an individual's performance and attendance. The Company has generally received union support in its implementation of reforms that impact quality, cost erosion and productivity improvements across all locations.
OUTLOOK
The Company expects to take advantage of being an established automaker and reap benefits from the expected growth of GDP and also form the proposed increase in automobile sector impact in GDP. Also, increase impact in global market is expected with increase of Indian automobile sector's global market size. The Company is preparing to align with National Electric Mobility Mission 2017 and also with Automobile Mission 2017, in BS5 and BS6 standards.
With government providing financing infrastructure in rural areas, the Company plans to take better advantage of this opportunity. Also, improvements in highway infrastructure will benefit the Company's subsidiaries like TATA Hitachi.
The Company is prepared with BSIV standard infrastructure and plans to proactively work for BSV and BSVI standards to be applicable in 2019 and 2023, respectively.
The Company is preparing itself to be efficient in not only BSIV, BSV and BSVI, but also plans to take a holistic approach towards environment regulations and stay ahead in Industry. The emergence of diverging markets and mis-alignment in production and supply at global level, will be strategically dealt with the help of wide network of subsidiaries and Joint ventures. The emergence of digital platforms for purchasing the Automobiles gives an opportunity to venture into an unexplored sector.
Continued investment, by Jaguar Land Rover, in new products and technologies as well as expanding its production capacity in appropriate strategic locations, while balancing production with sales, is key for the success of the Company.
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT
Statements in the Management Discussion and Analysis describing the Company's objective, projections, estimates and expectations may be "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of applicable securities laws and regulations. Actual results could differ materially from those expressed or implied. Important factors that could make a difference to the Company operations include, among others, economic conditions affecting demand/supply and price conditions in the domestic and overseas markets in which the Company operates, changes in government regulations, tax laws and other statutes and incidental factors.