Conservation of natural resources has always been a priority for Tata Motors. We strive to minimise the impact of our operations on the natural environment.
Depending upon stakeholder engagement outcomes and materiality assessment, we formulate our Sustainability Strategy and prioritise actions towards addressing the Material Environmental Issues. Our efforts on environmental conservation are governed by the Board-level Safety, Health and Environment (SHE) Committee, which monitors and reviews our environmental performance.
The key environmental issues which we prioritise and act upon are:
RESOURCE CONSERVATION
Resource optimisation is of prime importance. There are multiple financial and non-financial benefits, which are associated with resource optimisation. Not only does it lead to reduction in vehicular weight, fuel efficiency and generated waste, it leads to significant cost savings.
At TML, we achieved a significant reduction in steel and ferrous alloy consumption in FY 2016-17, compared to FY 2015-16, even though there has been an increase in production by 0.28%. We are continuously seeking to optimise material usage and recycling to avoid virgin material consumption through initiatives, such as using high-strength steel and alternate engineering plastic.
CIRCULAR ECONOMY
While we are complying with waste management laws in our respective geographies, we are actively working towards adopting the principles of 'Circular Economy'. This initiative will help us transform our approach towards waste management. It will build synergies among different functions such as design, materials sciences, engine technologies; and also present opportunities from new business streams.

Through Tata OK and Tata Assured initiative and our reconditioning business, Prolife, we are extending the life of our products, while ensuring optimum operational performance and minimising the usage of virgin materials.
14,058
Number of vehicles refurbished and sold
44,069
Total volume of product recycled/reused in take-back programme
JAGUAR LAND ROVER
Closed Loop Process
Continuing its efforts of building closed-loop systems, JLR has changed the way it works by collecting the surplus aluminium from its body-stamping process and reusing it to make new vehicles. This has helped in achieving Zero Waste to Landfill by 2016.
In one year alone, JLR reclaimed 50,000+ tonnes of press shop aluminium waste which was enough to make around 200,000 Jaguar XE body shells. The company is now applying this process to other materials.
Natural or sustainable materials
As a member of the Lightweight And Sound consortium (LANDS), JLR has been involved in a three-year project to find material replacements that use recycled content and that are suitable for current production methods. The work JLR is doing with its LANDS partners has confirmed that natural or sustainable materials can meet current automotive standards and be manufactured successfully – an important step towards further environmental improvements across the vehicle life cycle.
WATER CONSERVATION
Water consumption has been identified as one of our key sustainability issues. The water demand at nearly all our operational locations is significant owing to several water intensive processes. Besides, large quantity of water is used for non-industrial activities owing to our large workforce. Water productivity is also one of the key criteria for selecting any new technology.
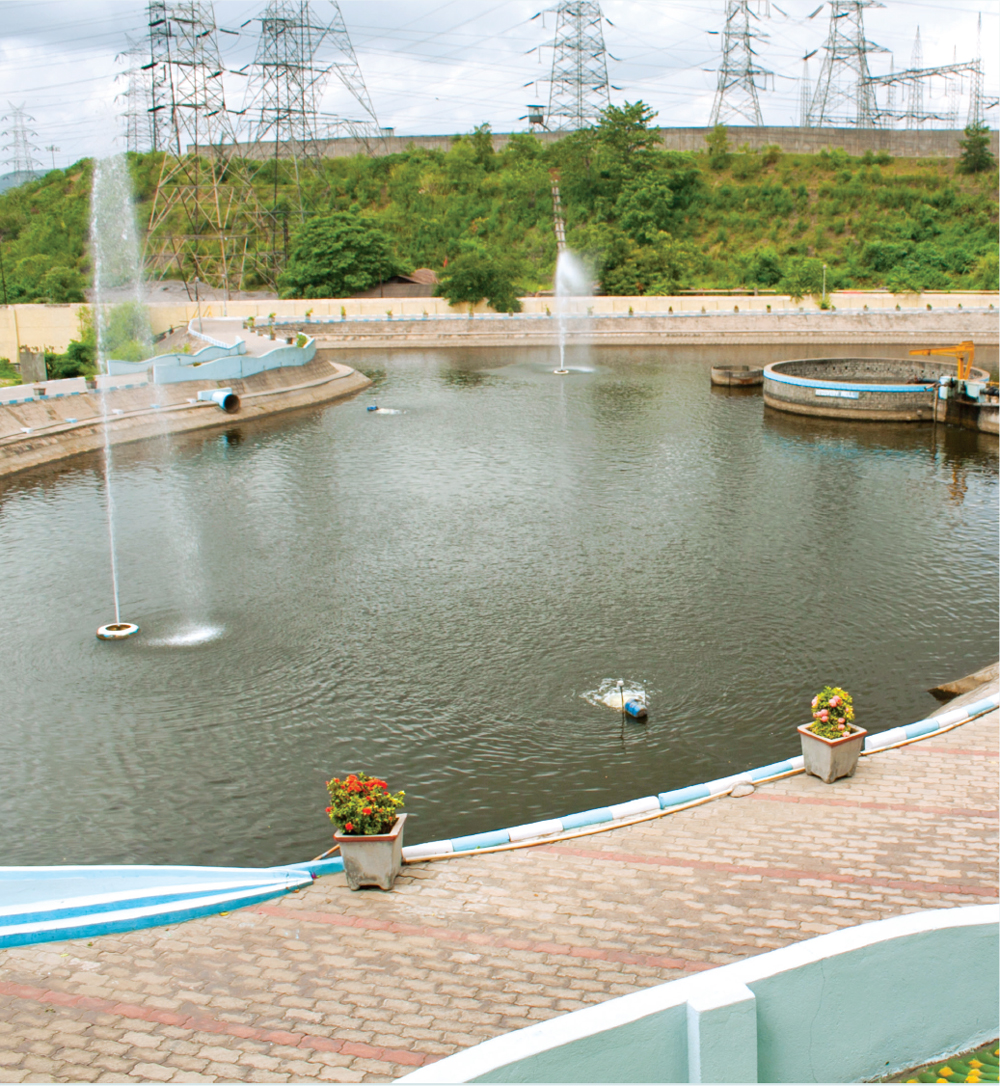

Some of our key conservation initiatives comprise:



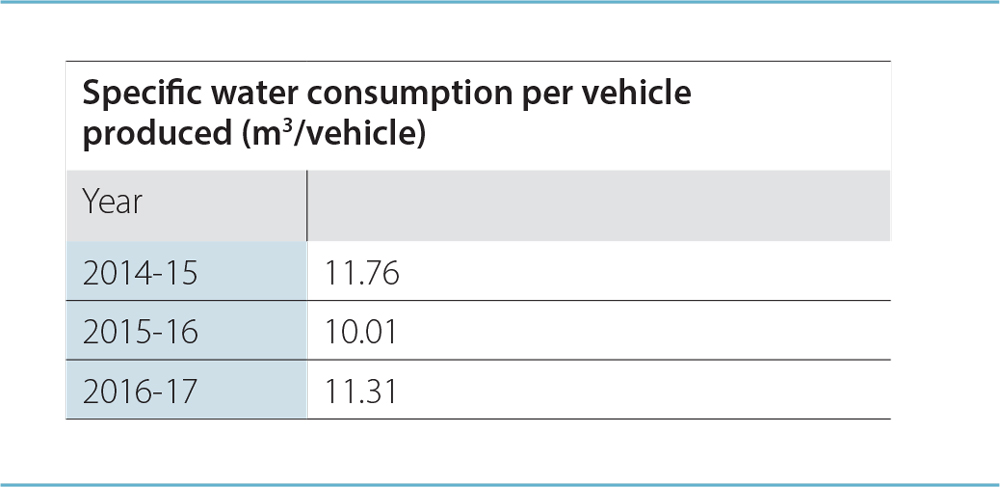
Currently, all TML manufacturing sites and subsidiaries, have achieved Zero Liquid Discharge status, except TML Jamshedpur where treated wastewater is partly reused.

The Jaguar Land Rover operations, too, are focused on reducing water use per vehicle. Since 2007, the Company has reduced water use per vehicle by 39%, through the 'water switch-off' initiative between vehicles on the production line.
We have achieved a significant reduction in surface water withdrawal due to rainwater harvesting and storage.
WASTE MANAGEMENT
With a flurry of in-house manufacturing activities such as pressing/stamping, fabrication, painting, machining, assembly and testing of aggregates to final assembly of vehicles, the waste-burden generated is huge. However, we are committed to diverting hazardous wastes away from destructive disposal practices and hence we are exploring multiple recycling options.
Some initiatives comprise energy recovery from high calorific value wastes through co-processing route with cement industries, solidification/stabilisation of ETP sludge as pavers and conversion of paint sludge into industrial primer.
BIODIVERSITY
Although our Indian manufacturing facilities are not located within the vicinity of any identified or notified bio-diversity hotspots or protected water bodies, the extended positive impacts of our water conservation efforts are evident with the variety of avian fauna seen at our water harvesting ponds.
During 2016-17, TML has taken multiple initiatives towards our journey to achieve 'Zero waste to common waste disposal site' and have reduced hazardous waste disposal to landfill and incineration. We significantly increased hazardous waste co-processing for energy recovery and material recovery at our various manufacturing sites as well as material recovery through recycling.
Progressing with 'Zero Waste' target by 2020, Jaguar Land Rover has set the interim target of zero waste to landfill from its manufacturing and product creation sites. Some of the key milestones for achieving the target include:
- No waste sent direct to landfill from vehicle operations
- 95% avoidance of landfill at second tier
The Company decided against sending the waste to off-site facilities for processing, which may already have an ongoing contribution to landfill.
ENERGY AND GHG EMISSIONS
In line with the Tata Group Policy on Climate Change, Tata Motors has articulated its Climate Change Policy, which articulates a three-pronged approach to our carbon emissions mitigation strategy:
Product Development
Minimising tail-pipe emissions, creating products dependent on alternative energy sources
Manufacturing Process
Improving energy efficiency and maximising use of renewable energy sources, thereby minimising emissions
Supply Chain
Minimising emissions with the life-cycle approach

There are numerous energy conservation initiatives undertaken by TML at its manufacturing facilities. Some of these include:
- Using infrared sensors and timers for on-off control of industrial equipment like fans/pumps/motors, among others.
- Installing Waste Heat Recovery System to recover waste heat from exhaust flue gases.
- Installing LED lighting in all offices and other common areas.
- Installing variable frequency drives.
TML is the second Indian company which is committed to RE100, a global collaborative initiative of the world’s most influential companies aspiring to source 100% renewable power.
Currently, TML has obtained around 9% of electricity from renewables and has its own captive wind power project of 21.95MW capacity.
JLR achieved a 32% reduction in its European fleet's average tailpipe CO2 emissions in just eight years. In the same period, it has driven a 38% improvement in its operational CO2 emissions. Through a combination of low-emission technologies and electrification, JLR's target is to reduce its European fleet's average tailpipe CO2 emissions by a further 25% by 2020.
Through REALCAR (Recycled Aluminium Car) project, in one year alone, JLR reclaimed and recycled 50,000+ tonnes of aluminium waste, feeding it back into its manufacturing process; and preventing the associated CO2 from being released into the atmosphere.
SETTING NEW BENCHMARKS
JLR continues to set new benchmarks for the sector. Targeting emissions reduction, both for the manufacturing process and during the vehicles' operations, JLR has undertaken multiple initiatives:
- UK manufacturing facilities, product creation sites and most of the satellite sites purchase 100% renewable electricity from electricity providers.
- Installing solar panels, LED lighting, combined heat and power, building management systems, voltage optimisation, insulation and energy mapping are all initiatives taken to ensure carbon neutrality by 2020.
- With an investment of GBP 23 million, the Company has implemented over 60 energy-saving projects over past few years, which has led to the savings of 57,000 tonnes of CO2 equivalent. With this accomplishment, JLR's specific emissions per vehicle has reduced by almost 38%, compared to what it was a decade ago.