Other financial liabilities
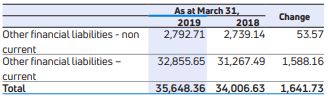
These included Rs.7,404.97 crores of derivative financial instruments, mainly attributable to Jaguar Land Rover as at March 31, 2019 compared to Rs.8,657.86 crores as at March 31, 2018, reflecting favorable foreign exchange movement between US$ and GB£. Further, liability for capital expenditure decreased to Rs.7,046.74 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.8,219.45 crores as at March 31, 2018. These decreases were offset by increase in current maturities of long-term borrowings to Rs.15,051.41 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.10,956.12 crores as at March 31, 2018.
Trade payables were Rs.68,513.53 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.72,038.41 crores as at March 31, 2018. The number of day’s payable outstanding is 110 days in FY 2018-19 compared to 121 days in FY 2017-18. The Consolidated cash conversion cycle indicates the time, the Company takes to collect cash from sale of inventory. It is calculated as trade receivables (in days) plus inventory (in days) less trade payable (in days). The status as at March 31, 2019 and 2018, is as follows:
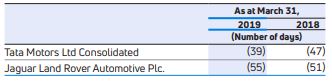
Acceptances were Rs.3,177.14 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.4,901.42 crores as at March 31, 2018
Provisions (current and non-current) were made towards warranty and employee benefit schemes. Short-term provisions are those, which are expected to be settled during next financial year. The details are as follows:
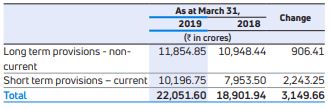
- Provision for warranty increased to Rs.17,501.26 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.15,935.10 crores as at March 31, 2018, an increase of Rs.1,566.16 crores primarily at JLR.
- The provision for employee benefits obligations increased to Rs.1,934.22 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.844.64 crores as at March 31, 2018. The increase is due to provisions for employee separation cost at JLR of Rs.954.40 crores.
- Provision for legal and product liability increased to Rs.1,786.43 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.1,319.87 crores as at March 31, 2018.
- Capital expenditure (net) was at Rs.35,236.29 crores in FY 2018-19, compared to Rs.35,048.62 crores, related mainly to capacity/ expansion of facilities, quality and reliability projects and product development projects.
- Net investments, short-term deposits, margin money and loans given was an inflow of Rs.14,532.42 crores in FY 2018-19 as compared to inflow of Rs.6,359.13 crores in FY 2017-18, mainly at Jaguar Land Rover.
- In FY 2018-19, Rs.12,755.97 crores were raised from longterm borrowings (net) as compared to Rs.4,557.96 crores (net) in FY 2017-18 as described in further detail below
- Net increase in short-term borrowings of Rs.3,174.23 crores in FY 2018-19 as compared to Rs.2,960.35 crores in FY 2017-18, mainly at Tata and other brand vehicles (including vehicle financing).
Other liabilities
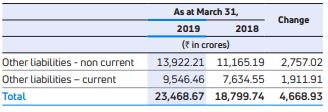
These mainly includes liabilities towards employee benefits obligations of Rs.6,110.12 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.4,100.76 crores as at March 31, 2018, increase mainly at Jaguar Land Rover. Contract liabilities were Rs.9,250.47 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.7,867.89 crores as at March 31, 2018. Statutory dues (VAT, Excise, Service Tax, Octroi etc.) were Rs.3,913.94 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.3,176.86 crores as at March 31, 2018. Government Grants increased to Rs.3,278.37 crores as at March 31, 2019 as compared to Rs.2,976.65 crores as at March 31, 2018.
Consolidated Cash Flow
The following table sets forth selected items from consolidated cash flow statement:
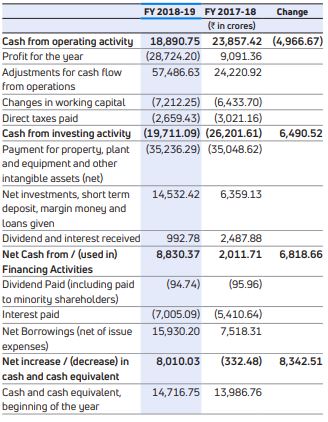
Cash generated from operations before working capital changes was Rs.28,762.43 crores in FY 2018-19, as compared to Rs.33,312.28 crores in the previous year, representing a decrease in cash from generated from consolidated operations. After considering the impact of working capital changes including the net movement of vehicle financing portfolio, the net cash generated from operations was Rs.18,890.75 crores in FY 2018-19, as compared to Rs.23,857.42 crores in the previous year. The increase in finance receivables offset by decrease in trade receivables, inventories and other assets, amounting to Rs.6,515.44 crores mainly due to increase in sales was coupled with decrease in trade and other payables and provisions amounting to Rs.696.81 crores.
The net cash outflow from investing activity decreased to Rs.19,711.09 crores in FY 2018-19 from Rs.26,201.61 crores in FY 2017-18.
The net change in financing activity was an inflow of Rs.8,830.37 crores in FY 2018-19 as compared to Rs.2,011.71 crores in FY 2017-18.
There has been a net outflow in the Free cash flows of Rs.16,345.54 crores due to lower growth and higher investments in Jaguar Land Rover.
As at March 31, 2019, the Company’s borrowings (including shortterm debt) were Rs.1,06,175.34 crores, compared to Rs.88,950.47 crores as at March 31, 2018..
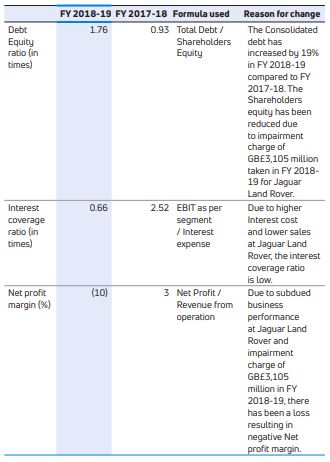
KEY FINANCIAL RATIOS
The details of significant changes (25% or more) in the key financial ratios in FY 2019 compared to 2018 is as follows:
Principal Sources of Funding Liquidity
The Company finances its capital expenditures and research and development investments through cash generated from operations, cash and cash equivalents, debt and equity funding. The Company also raises funds through sale of investments, including divestment in stakes of subsidiaries on a selective basis.
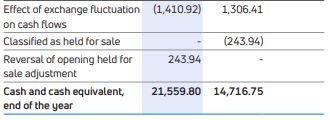
The Company’s cash and bank balances on a consolidated basis were Rs.32,648.82 crores as at March 31, 2019, as compared to Rs.34,613.91 crores as at March 31, 2018. These enable the Company to cater to business needs in the event of changes in market conditions.
The Company’s capital expenditures were Rs.36,635.67 crores and Rs.42,672.29 crores for FY 2018-19 and FY 2017-18, respectively, and it currently plans to invest approximately Rs.450 billion in FY 2018-19 in new products and technologies. The Company intends to continue to invest in new products and technologies to meet consumer and regulatory requirements. These investments are intended to enable the Company to pursue further growth opportunities and improve the Company’s competitive positioning
The Company expects to meet most of its investments out of operating cash flows and cash liquidity available. In order to meet the remaining funding requirements, the Company may be required to raise funds through additional loans and by accessing capital markets from time to time, as deemed necessary.
With the ongoing need for investments in products and technologies, the Company on a consolidated basis has free cash flow (a non-GAAP measure, measured at cash flow from operating activities, less payment for property, plant and equipment and intangible assets) negative in FY 2018-19, of Rs.16,346 crores. The cash flow from financing arm is negative Rs.7,177 crores. Net Automotive cash flow is negative Rs.9,169 crores. The Company expects that with the improvement in macro-economic conditions and business performance, through other steps like raising funds, review of non-core investments, and through appropriate actions for raising additional long-term resources, the funding gap can be appropriately addressed.
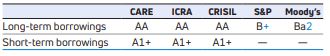
The following table provides information for the credit rating of Tata Motors Limited for short-term borrowing and long-term borrowing from the following rating agencies as at March 31, 2019: Credit Analysis and Research Ltd Ratings, or CARE, Information and Credit Rating Agency of India Ltd, or ICRA, Credit Rating Information Services of India Limited, or CRISIL Ltd, Standard & Poor’s Ratings Group, or S&P, and Moody’s Investor Services, or Moody’s. A credit rating is not a recommendation to buy, sell or hold securities. A credit rating may be subject to withdrawal or revision at any time. Each rating should be evaluated separately of any other rating:
The Company believes that it has sufficient liquidity available to meet its planned capital requirements. However, the Company’s sources of funding could be materially and adversely affected by an economic slowdown, as was witnessed in Fiscal 2009, or other macroeconomic factors in India and abroad, such as in the United Kingdom, the United States, Europe, Russia and China, all of which are beyond the Company’s control. A decrease in the demand for the Company’s vehicles could affect its ability to obtain funds from external sources on acceptable terms or in a timely manner
The Company’s cash is located at various subsidiaries within the Tata Motors Group. There may be legal, contractual or economic restrictions on the ability of subsidiaries to transfer funds to the Company in the form of cash dividends, loans, or advances. Brazil, Russia, South Africa and other jurisdictions have regulatory restrictions, disincentives or costs on pooling or transferring of cash. However, such restrictions have not had and are not estimated to have a significant impact on the Company’s ability to meet its cash obligations.
In order to refinance the Company’s borrowings and for supporting long-term fund needs, the Company continued to raise funds in FY 2017-18 and 2019, through issue of various debt securities and loans as described below.
The Company successfully completed liability management exercise by part refinancing of US$500 million notes due for repayment on April 30, 2020. The Company raised ECB of US$237.468 million maturing in June 2025 which was used to repay the investors, who had surrendered their bonds through the tendering process.
During FY 2018-19, Tata Motors Limited raised unsecured term loans of Rs.1500 crores from banks for ongoing capital spending requirements
During FY 2018-19, JLR issued EUR500 million senior notes due in 2026 at a coupon of 4.50% per annum. JLR also raised US$1,000 million through syndicated loan. The proceeds were for general corporate purposes, including support for JLR’s ongoing growth and capital spending requirements.
During FY 2018-19, TMFHL and its subsidiaries, Tata Motors Finance Limited and TMFSL, raised Rs.2,066 crores (Face Value) by issuing NCDs. Bank borrowings through secured term loans continued to be a major source of funds for long-term borrowing and raised Rs.6,306 crores during FY 2018-19. TMFL has also done securitization of Rs.3,862 crores in FY 2018-19.
The Tata Motors Group funds its short-term working capital requirements with cash generated from operations, overdraft facilities with banks, short-and medium-term borrowings from lending institutions, banks and commercial paper. The maturities of these short-and medium-term borrowings and debentures are generally matched to particular cash flow requirements. The working capital limits are Rs.10,000 crores from various banks in India as at March 31, 2019. The working capital limits are secured by hypothecation of certain existing current assets of the Company. The working capital limits are renewed annually.