Jaguar Land Rover’s Sales & Distribution
As at March 31, 2019, Jaguar Land Rover distribute its vehicles in 120 markets for Jaguar and 128 markets for Land Rover globally. Sales locations for vehicles are operated as independent franchises. Jaguar Land Rover are represented in its key markets through its National Sales Company’s (“NSC’s”) as well as thirdparty importers. Jaguar and Land Rover have regional offices in certain select countries that manage customer relationships and vehicle supplies and provide marketing and sales support to their regional importer markets. The remaining importer markets are managed from the United Kingdom.
Jaguar Land Rover products are sold through a variety of sales channels: through its dealerships for retail sales; for sale to fleet customers, including daily rental car companies; commercial fleet customers; leasing companies; and governments. Jaguar Land Rover do not depend on a single customer or small group of customers to the extent that the loss of such a customer or group of customers would have a material adverse effect on its business.
As at March 31, 2019, Jaguar Land Rover global sales and distribution network comprised 23 NSCs, 77 importers, 2 export partners and 2,684 franchise sales dealers, of which 1,299 are joint Jaguar and Land Rover dealers.
Jaguar Land Rover — Competition
Jaguar Land Rover operates in a globally competitive environment and faces competition from established premium and other vehicle manufacturers who aspire to move into the premium performance car and premium SUV markets, some of which are much larger than they are. Jaguar vehicles compete primarily against other European brands such as Audi, Porsche, BMW and Mercedes Benz as well as Tesla. Land Rover and Range Rover vehicles compete largely against SUVs from companies such as Audi, BMW, Infiniti, Lexus, Mercedes Benz, Porsche, Volvo and Volkswagen.
Jaguar Land Rover — Seasonality
Jaguar Land Rover volumes are impacted by the biannual change in agerelated registration plates of vehicles in the United Kingdom, where new agerelated plate registrations take effect in March and September. This has an impact on the resale value of the vehicles because sales are clustered around the time of the year when the vehicle registration number change occurs. Seasonality in most other markets is driven by the introduction of new model year vehicles and derivatives. Furthermore, Western European markets tend to be impacted by summer and winter holidays, and the Chinese market tends to be affected by the Lunar New Year holiday in either January or February, the PRC National Day holiday and the Golden Week holiday in October. The resulting sales profile influences operating results on a quarter-to-quarter basis.
Other Operations Overview
The Company’s other operations business segment mainly includes information technology services, machine tools and factory automation services. The Company’s revenue from other operations before inter-segment eliminations was Rs.3,626.07 crores in FY 2018-19, an increase of 11.5% from Rs.3,252.36 crores in FY 2017- 18. Revenues from other operations represented 1.2% and 1.1% of total revenues, before inter-segment eliminations, in FY 2018-19 and FY 2017-18.
OPPORTUNITIES:
In the Budget 2019, the Government of India has allocated Rs.83k crore to highways among various infra-based sectors. Apart from National Highways, Centre upgraded fiscal spending on rural roads at Rs. 19k crore under Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY). Focus on road building under National Highway Authority of India and PMGSY will spur demand for commercial vehicles and tractors, respectively.
The Automotive Mission Plan 2016-26 aims at 12% share of automotive industry in GDP, along with implementation of BS6 vehicles by 2023 for four wheelers. Budget 2019 saw for the first time, government’s intent to have electric mobility by 2030. The Faster Adoption And Manufacturing of (Hybrid) & Electric (FAME) Vehicles in India lays down the roadmap to support the development of electric and hybrid vehicles market and its manufacturing eco-system with a view to achieve selfsustenance as early as 2020. Technology development, demand creation, pilot projects and charging infrastructure are the focus areas of the scheme.
Jaguar Land Rover has a strong product range that compete in various segments, including the increased electrification of the product portfolio. New and refreshed products, including the Range Rover Velar (on sale since July 2017), the Jaguar E-PACE (on sale since November 2017) and the all-electric Jaguar I-PACE (on sale since June 2018) as well as the refreshed Range Rover and Range Rover Sport (including hybrid models), the recently announced new Defender and other new and refreshed products, ensures that Jaguar Land Rover can compete in the premium segments with class-leading products.
FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE ON A CONSOLIDATED BASIS
The financial information discussed in this section is derived from the Company’s Audited Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Company has adopted Ind AS 115 with a modified retrospective approach. The Company makes transport arrangements for delivering its vehicles to the dealers. The gross consideration received in respect of these arrangements was recognized and presented with revenue in the statement of profit and loss. The costs associated with these arrangements were presented within freight cost in the statement of profit and loss. In accordance with Ind AS 115, the Company has determined that it is an agent in providing these services, and therefore the gross consideration received, net off cost associated with respect to these arrangements is presented within revenue effective April 1, 2018. Certain payouts made to dealers such as infrastructure support payments are to be treated as variable components of consideration and are therefore in accordance with Ind AS 115, recognized as revenue deductions in future. These changes in presentation in the income statement has resulted in decrease in both revenues and expenses by Rs. 3,809.03 crores for the year ended March 31, 2019.
Overview
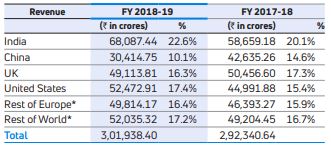
The Company income from operations including finance revenues increased by 3.3% to Rs. 3,01,938.40 crores in FY 2018-19 from Rs. 2,92,340.64 crores in FY 2017-18. The increase is mainly attributable to better sales volumes of the Company’s India business and favourable currency translation from GB£ to INR of Rs. 14,516.58 crores, offset by lower sales of Jaguar Land Rover.
The Company has pursued a strategy of increasing exports of Tata and other brand vehicles to new and existing markets. Tata Technologies Ltd (TTL), subsidiary of the Company, witnessed increase in revenue due to favourable currency movement, which helped in growth of revenue in the UK, Europe and North America. The growth in Asia Pacific revenue of TTL was primarily driven by strong revenue growth in India and China in key accounts and growth in educational product sales. However, due to lower sales of JLR and increased growth in revenue in India in FY 2018-19, the proportion of the Company’s net sales earned from markets outside of India decreased to 77.4% in FY 2018-19 from 79.9% in FY 2017-18. Further, in FY 2018-19, the revenue of the Company’s subsidiary in South Korea, TDCV, has been lower due to lower industry volumes and aggressive discounting and marketing strategy of importers. The following table sets forth the Company’s revenues from its key geographical markets and the percentage of total revenues that each key geographical market contributes for the periods indicated:
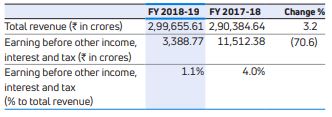
Earnings before other income, interest and tax, were Rs. 3,774.03 crores in FY 2018-19 compared to Rs. 11,787.51 crores in FY 2017-18. The decrease was primarily driven by the performance of Jaguar Land Rover business, including higher depreciation and amortization, fixed marketing expenses/selling costs. The Company’s net loss (attributable to shareholders of the Company) was Rs. 28,826.23 crores in FY 2018-19 as compared to a profit of Rs. 8,988.91 crores in FY 2017-18. In FY 2018-19, the Company has taken an impairment charge of £3,105 million (Rs. 27,837.91 crores). The Company assessed the recoverable amount of the Jaguar Land Rover business, which represent a single cash-generating unit (CGU), as the higher of Fair Value Less Cost of Disposal (‘FVLCD’) and Value in Use (‘VIU’) of the relevant assets of the CGU, due to weaker sales and profitability, change in market conditions especially in China, technology disruptions.
The Company’s operations is divided into automotive operations and other operations as described further below.
A core initiative of the Company was the implementation of the Organization Effectiveness (OE) program, a strategic program designed to overhaul and transform the Company.
Pursuant to the changes implemented as a result of the OE program, the Company has drawn separate strategies for commercial vehicles, passenger vehicles and financing business from FY 2018-19. Consequent to these changes, commencing FY 2018-19, the reportable segments is as follows:
- Automotive: The Automotive segment consist of four reportable sub-segments: Tata Commercial Vehicles, Tata Passenger Vehicles, Jaguar Land Rover and Vehicle Financing
- Others: Others consist of IT services and machine tools and factory automation solutions.
Tata Commercial vehicles include commercial vehicles manufactured under Tata and Daewoo brands. Tata passenger vehicles include passenger vehicles manufactured under Tata and Fiat brands and excludes vehicles manufactured under Jaguar Land Rover brands. Vehicle Financing which is Tata Motors Finance include financing of Tata and Jaguar Land Rover new vehicles, pre-owned vehicles including other OEMs brands and corporate lending to the Company’s channel partners.
The Company believe that this reorganization will improve speed, agility and simplicity within our business units, and enable strong functional leadership, improved decision-making, quicker responses to changing market conditions and clear accountability.
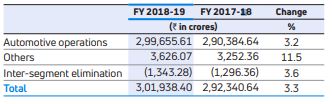
The table below sets forth the breakdown in revenues between the Company automotive operations and other operations in FY 2018-19 and FY 2017-18 and the percentage change from period to period.
Automotive operations
Automotive operations are the Company most significant segment, accounting for 99.2% and 99.3% of the Company’s total revenues in FY 2018-19 and FY 2017-18 respectively. In FY 2018-19, revenue from automotive operations before inter-segment eliminations was Rs. 2,99,655.61 crores as compared to Rs. 2,90,384.64 crores in FY 2017-18, an increase of 3.2%.
The following table sets forth selected data regarding the Company’s automotive operations for the periods indicated, and the percentage change from period to period (before inter-segment eliminations).
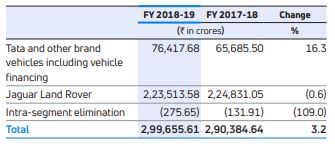
The Company’s automotive operations segment is further divided into Tata and other brand vehicles, Vehicle financing and Jaguar Land Rover. In FY 2018-19, Jaguar Land Rover contributed 75% of the Company’s total automotive revenue compared to 77% in FY 2017-18 and the remaining 25% was contributed by Tata and other brand vehicles and Financing in FY 2018-19 compared to 23% in FY 2017-18.
The Company’s revenue from Tata and other brand vehicles (including vehicle financing) and Jaguar Land Rover in FY 2018- 19 and FY 2017-18 and the percentage change from period to period (before intra-segment eliminations) is set forth in the table below.
The Tata and other brand vehicles including vehicle financing consists of following categories:
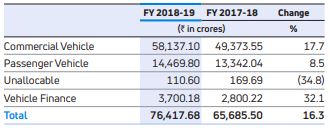
Other operations
The following table sets forth selected data regarding the Company’s other operations for the periods indicated and the percentage change from period to period (before inter-segment eliminations).
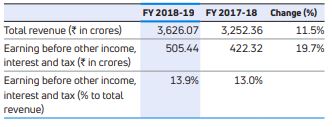
The other operations business segment includes information technology, machine tools and factory automation solutions. In FY 2018-19, revenue from other operations before inter-segment eliminations was Rs.3,626.07 crores compared to Rs.3,252.36 crores in FY 2017-18. Results for the other operations business segment before other income, finance cost, tax and exceptional items (before inter-segment eliminations) were Rs.505.44 crores in FY 2018-19 as compared to Rs.422.32 crores for FY 2017-18.