PRINCIPLE 3 Employee Wellbeing
- Please indicate the Total number of employees.
52,979 as at 31st March, 2018 (Includes Permanent, Temporary, trainee and contractual employees).
- Please indicate the Total number of employees hired on temporary/contractual/casual basis.
28,057 as at 31st March, 2018.
- Please indicate the Number of permanent women employees.
689 as at 31st March, 2018.
- Please indicate the Number of permanent employees with disabilities
12 as at 31st March, 2018.
- Do you have an employee association that is recognized by management?
The manufacturing plants at Jamshedpur, Pune, Lucknow, Pantnagar and Sanand have employee unions recognized by the management. The Company enters into long term wage settlements with these recognized unions.
- What percentage of your permanent employees is members of this recognized employee association?
Around 94% of the operative employees at Jamshedpur, Pune, Lucknow, Pantnagar & Sanand plants are members of these employee unions. These employees represent around 52% of the total permanent employees at these five plants. The Company do not have an Employees Union at our Dharwad Plant presently.
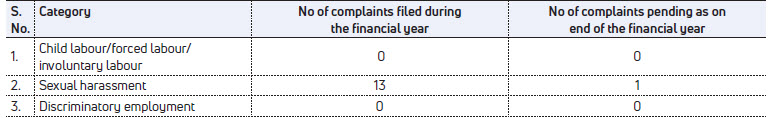
- Please indicate the Number of complaints relating to child labour, forced labour, involuntary labour, sexual harassment in the last financial year and pending, as on the end of the financial year.
- What percentage of your under mentioned employees were given safety & skill up-gradation training in the last year?
- Permanent Employees
- Permanent Women Employees
- Casual/Temporary/Contractual Employees
- Employees with Disabilities
Safety is of paramount importance to the Company. All semployees of the Company are provided with safety training as part of the induction programme. The safety induction programme is also a compulsory requirement for contract workforce before they are inducted into the system. TheCompany has a structured safety training agenda on an ongoing basis to build a culture of safety across its workforce. The Company believes in continual learning of its employees and has institutionalized a continual learning model for skill upgradation, especially at the shop-floor level. The learning and development needs of management cadre employees are met through the Company’s L&D structure which includes various training delivery mechanisms.
PRINCIPLE 4: Stakeholder Engagement
- Has the company mapped its internal and external stakeholders?
Yes. The Company has mapped its internal and external stakeholders. It uses both formal and informal mechanisms to engage with various stakeholders to understand their concerns and expectations. Individual departments within the organization have roles and responsibilities identified and defined to engage with various stakeholders.
- Out of the above, has the company identified the disadvantaged, vulnerable & marginalized stakeholders?
Yes. The Company’s AA policy is specially designed to address the socially disadvantaged sections of the society, Scheduled Castes and Tribes. Within the broader stakeholder group of communities, the Company works towards women empowerment and education of children. Every year, the Company participate in TAAP (Tata Affirmative Action Program) Assessment, developed on the lines of TBEM.
- Are there any special initiatives taken by the company to engage with the disadvantaged, vulnerable and marginalized stakeholders. If so, provide details thereof, in about 50 words or so.
Our CSR programmes and projects are aimed at serving the needy, deserving, socio-economically backward and disadvantaged communities aimed at improving the quality of their lives. Under TAAP, the Company continues to serve the SC and ST communities in inter alia Education, Employability and Entrepreneurship.

PRINCIPLE 5: Human Rights
- Does the policy of the company on human rights cover only the company or extend to the Group/Joint Ventures/ Suppliers/Contractors/NGOs/Others?
The Company respects human rights and has established a Policy on Human Rights. The policy details the Company’s approach towards human rights and sets the Company’s expectations of its Channel Partners and Contractors to adhere to principles of human rights. The Company encourages its suppliers, vendors, contractors and other business partners associated with the Company to follow the principles laid out in the TCoC.
- How many stakeholder complaints have been received in the past financial year and what percent was satisfactorily resolved by the management?
During Fiscal 2018, 57 concerns have been received towards actual or potential violation of TCoC, of which 51 of the complaints were satisfactorily resolved as at 31.03.2018.
PRINCIPLE 6: Environmental
- Does the policy related to Principle 6 cover only the company or extends to the Group/Joint Ventures/Suppliers/Contractors/NGOs/others.
Sustainability is built into the Company business processes through well-defined Sustainability Policy. This policy reaffirms value system committed to integrate environmental, social and ethical principles into our business and innovate sustainable mobility solutions with passion to enhance quality of life of communities.
The Company also has Environmental Procurement Policy which is applicable to all its vendors, contractors and service providers. - Does the company have strategies/initiatives to address global environmental issues such as climate change, global warming, etc.? Y/N. If yes, please give hyperlink for webpage etc.
Yes, the Company has Climate Change policy which guides the organizational efforts towards mitigating and adapting to climate change. The Company approach towards climate change mitigation and pursuing low carbon growth is threefold– develop cleaner and more fuel efficient vehicles, reduce environmental impacts of manufacturing operations and build awareness among stakeholders. The Company also continually working on alternate fuel technologies like electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles and fuel cell technologies. The Company has delivered 25 ‘Tata Starbus Hybrid Electric Bus’ to Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA) and has also delivered the first set of Tigor Electric Vehicles (EVs) to state-run Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL) as part of their initiative to procure 10,000 electric vehicles.
The Tata Group became part of the Prime Minister’s Low Carbon Committee and was a member in the Steering Committee of the ‘Caring for Climate’ initiative of the United Nations Global Compact and United Nations Environment Programme. Ahead of the crucial global climate change talks that concluded in Paris, global corporate leaders signed an open letter on climate change.
- Does the company identify and assess potential environmental risks? Y/N
Yes, the Company has a Sustainability Policy and Environmental Policy which guides the Company’s efforts to minimize its environmental impacts and continually improve the environmental performance across life cycle of the product. All manufacturing plants in India are certified to Environmental Management Systems (EMS) as per ISO 14001. As part of EMS implementation, potential environmental risks are identified and appropriate mitigation strategies are planned.
- Does the company have any project related to Clean Development Mechanism? If so, provide details thereof, in about 50 words or so. Also, if yes, whether any environmental compliance report is filed?
None of our plants have undertaken Clean Development Mechanism projects during Fiscal 2018.
- Has the company undertaken any other initiatives on - clean technology, energy efficiency, renewable energy, etc.? Y/N. If yes, please give hyperlink for web page etc.
In Fiscal 2018, the Company continued to work on improving energy efficiency, introduction of clean technology and increasing its renewable energy consumption in line with our aspiration to RE100 - which is a collaborative, global initiative of influential businesses aspiring to source 100% renewable electricity for operations.
(A) Renewable Energy
During Fiscal 2018, the Company has set up in-house Renewable Electricity (RE) generation capacity (solar and wind) which includes:
- 21.95 MW Captive Wind Power project at Supa and Satara in Maharashtra;
- 2 MW Roof-top Solar PV plant at Sanand Works;
- 2.1 MW Roof-top Solar PV installation at Pune Works and work is ongoing for additional 2MW installation;
- 2 MW Solar PV installation at Lucknow Works;
- 18.5 kWp Solar PV installation at Pantnagar Works; and
- 7.2 kW hybrid wind and solar energy system at Dharwad Works.
The Company sources off-site wind power at its Pune, Sanand and Dharwad Works through Power Purchase Agreements (PPA) with Third Party Wind Power Generators. It would continue to source renewable power from the grid in line with regulatory policies / frameworks and tariffs in the States where we operate.
In Fiscal 2018, the Company generated / sourced a total 99,382 MWh of RE for its manufacturing operations which contributed to financial saving of Rs.666.3 Lakhs.
(B) Energy Efficiency / Clean Technology
The Company has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power, Government of India to achieve energy saving and resource conservation byimplementing various energy efficiency initiatives across the Company’s manufacturing facilities in India. Phase I of the project is being rolled-out at our Pantnagar, Lucknow and Pune plants and will be extended later to other plants. Key highlights of the MoU include - Diagnostic Studies & Pilot Projects, Implementation of Energy Efficiency Projects through innovative financial models and Capacity Building & Training.
The Company has also implemented significant Energy Conservation projects across its manufacturing plants and offices in Fiscal 2018.
- Pune Plants optimized power consumption in ventilation systems at Engine Shop, installed energy efficient LED lighting systems, converted washing machines from electrical to natural gas heating, provided interlocks and auto switch-off timers in Engine Shop, installed Intelligent Flow Control in Compressor for Paint Shop operations and integrated painting operations into a single shop.
- Jamshedpur Plant optimized engine test bed utilization and installed energy efficient LED lighting.
- Sanand Plant optimized use of Air Supply Plants (ASP’s), washing process in Head & Block at Engine Shop, replaced Nd-YAG laser with fiber laser, and provided interlocks and auto switch-off timers for
- Lucknow Plant implemented empty skid storage facility in Paint Shop and installed energy efficient LED lighting.
- Pantnagar Plant contributed by reduction in no-load losses in transformers and installed energy efficient LED lighting.
- Are the Emissions/Waste generated by the company within the permissible limits given by CPCB/SPCB for the financial year being reported?
The Company is in compliance within the prescribed permissible limits as per CPCB/SPCB for air emissions, effluent quality and discharge, solid and hazardous waste generation and disposal.
- Number of show cause/legal notices received from CPCB/SPCB which are pending (i.e. not resolved to satisfaction) as on end of Financial Year.
There is no show cause /legal notice from CPCB/SPCB pending resolution by the Company as on end of Fiscal 2018..
Please refer Annexure 2 to Board’s Report of the Company Annual Report FY 2017-18, ‘Energy and Climate Change’ and ‘Environmental Stewardship of the Tata Motors Sustainability Report 2017-18 for details on the Company’s energy efficiency and cleaner production initiatives.